水凝胶是一类的软湿材料,但是其自身的强度问题则限制其在许多领域的应用。提高水凝胶的强度一直是水凝胶研究领域的热点之一。在以往的一些研究中,通过各种设计策略也很难将水凝胶的拉伸强度提高到几十兆帕的级别。实现水凝胶的拉伸强度达到几十兆帕是一个很大的挑战。
中国科学院兰州化学物理研究所周峰研究员领导的课题组在其先前报道的工作基础上(Advanced Materials.2015,27(12),2054~2059),使用简单的预拉伸下构筑第二物理交联网络的方法制备的双交联水凝胶,在其预拉伸方向上的拉伸强度可以超过40 MPa,并且其弹性模量也大于40MPa,断裂拉伸应变超过200%,相关论文发表于Small,2016,DOI:10.1002/smll.201601893 。
图1. 超高强度的各向异性水凝胶的制备简图
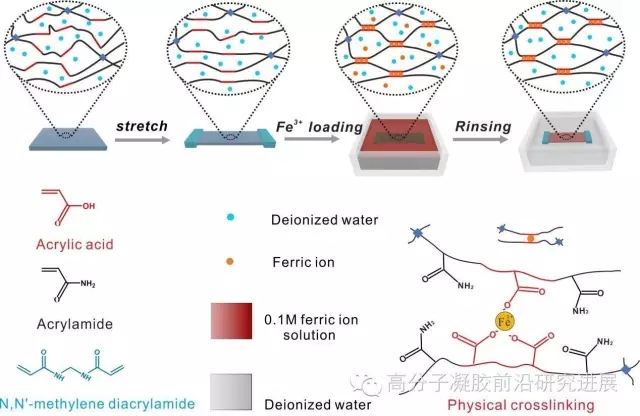
该超高强度水凝胶的制备方法十分简单,如图1所示,将制备好的化学交联PAAm-co-PAAc水凝胶预先拉伸到一定的应变,然后固定好后浸泡在铁离子溶液中,最后将水凝胶片浸泡在去离子水中以除去多余的铁离子。
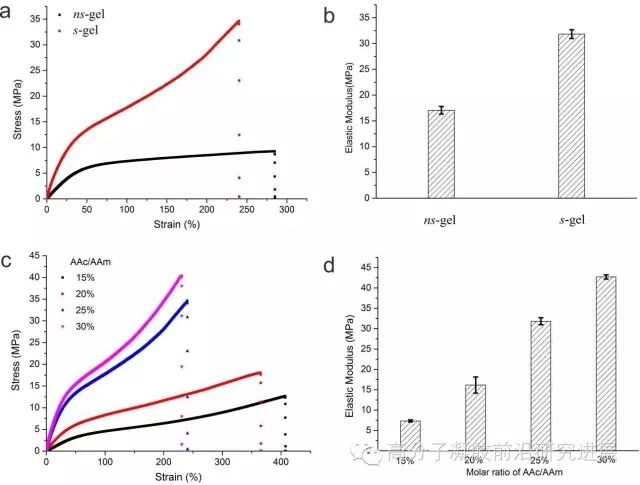
图2. 拉伸强度的表征:预拉伸方法制备的双交联水凝胶与空白样品之间的拉伸强度(a)与弹性模量(b)的比较;AAc/AAm的摩尔比率对拉伸强度(c)以及弹性模量(d)的影响
图2给出了预拉伸下制备的超高强度水凝胶与其空白样品的强度比较,从图2a可以看出,在预拉伸方向上,水凝胶的拉伸强度得到了极大的提高,并且弹性模量也相应增大。从而说明这种分子取向结构的保留,对于在与取向结构相同的方向上拉伸强度有很大的促进作用。该水凝胶的机械性能强度可调,可以通过调整优化实验参数获得不同强度的水凝胶。例如AAc/AAm的摩尔比率就会对该水凝胶的强度有很大的影响,从图2c中可以看出,随着丙烯酸在体系中的量的增大,其强度均有提高,在其比率为30%时,在与预拉伸相同的方向上的拉伸强度达到了40 MPa。
图3. 凝胶的各向异性机械性能

由于在拉伸的状态下,聚合物分子链会形成的一定的分子取向,该取向结构在形成第二层物理交联网络的时候被固定下来,从宏观的机械性能测试中,该水凝胶表现明显的力学性能各向异性,如图3所示。首先我们发现随着预拉伸的应变从50%增加到300%,其在与预拉伸方向相同的方向上的拉伸强度逐渐增大(图3a),而与预拉伸方向垂直的方向上断裂拉伸强度变化不大,而断裂应变则随着预拉伸的应变的增大而显著减小。
该方法简单易行,通过引入特殊的结构来进一步提高离子交联的双交联水凝胶的强度。通过预拉伸诱导形成分子取向再通过铁离子交联固定下来,所得的水凝胶强度得到很大的提升,并且具有非常明显的各向异性结构。该材料在水凝胶基人造肌肉等领域有潜在的应用价值。
周峰研究员课题组网页:http://www.licp.cas.cn/zfz/english/
原文摘要:
P Lin, T Zhang, X Wang, B Yu, F Zhou*
Small,2016,DOI:10.1002/smll.201601893
The poor mechanical strength of hydrogels has largely limited their wide applications, and improving hydrogels' mechanical strength is a hot and important topic in the hydrogel research field. Although many successful strategies have been proposed to improve hydrogels' mechanical strength during the past decades, a hydrogel with a tensile stress surpassing dozens of mega Pascal is desirable, yet still a big challenge. To address this issue, the Fe3+-mediated physical crosslinking formed under stretch conditions was employed in a chemically crosslinked poly (acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) network to achieve a dual-crosslinked hydrogel. The expected molecular orientation occurs under stretch and allows the maximumu chelating interaction between pendant carboxylic anions and Fe3+ and molecules conformation being frozen, leading to the mechanical strength improving dramatically. As a result, an unprecedentedly high mechanical strength, but anisotropic dual-crosslinked hydrogel was obtained. By optimizing the experimental parameters, the nominal tensile stress along pre-stretching direction can reach as high as ≈40 MPa with elastic modulus of ≈40 MPa at large strain (>200%). In addition, the molecular orientation also leads to big difference of mechanical performance between parallel and perpendicular direction.
————来源:高分子凝胶研究前沿进展



