智能驱动材料能够把外部刺激(如电、光、磁、热、化学等刺激)的能量转化为机械能,从而使材料发生可控的形状或体积变化,具有信息识别、传感、反馈、驱动等多种功能,在机械、航空、海洋、建筑和国防等领域展现出了非常广阔的应用前景。现有的驱动材料存在应力小、响应速度慢、回复率较低等问题。南开大学材料科学与工程学院研究团队设计并合成基于高分子弹性体和石墨烯的复合驱动材料,充分发挥二者的协同作用,构建了新型智能驱动“机器人”。
聚偏氟乙烯(Poly(vinylidene fluoride),PVDF)是一种很好的介电弹性体,在外电场作用下可改变体积或形状; 当外界刺激撤销后, 又能恢复到原始状态, 从而实现电场驱动,将电能转换成机械能。但这种材料有明显的缺点,其能量转换效率低,响应速度慢,应力小,并且需要很高的驱动电压,阻碍了其在诸多方面的应用。而石墨烯具有优良的机械性能,电学性能及物理化学稳定性,与PVDF性质互补。
南开大学研究人员将石墨烯和PVDF 的特点结合起来,充分发挥有机-无机材料体系的协同作用,设计并制备了石墨烯/PVDF 双层电驱动材料。利用石墨烯独特的大π共轭体系,突出其对外界电信号很强的响应性,同时结合PVDF优良的机械形变及回复性能,开发出具有低驱动电压,高形变量,超快速响应等特点的电驱动复合材料。该材料可以在低电压下产生大形变量,其响应速度在毫秒量级,远远超过现有的高分子驱动材料。
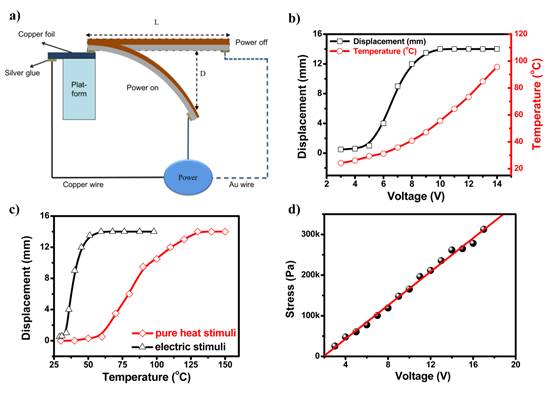
图1 石墨烯/PVDF材料的电致驱动
更重要的是,南开大学研究人员通过模拟海豚游泳的姿态,利用该驱动材料作为鱼模型的驱动部件,首次设计并制备了可在溶液中快速游动的电驱动“机器人”,获得了智能驱动材料领域的新突破。该项研究拓展了高分子智能材料和器件设计的新领域,在机械、航空、海洋、生物等领域具有很好的应用前景。
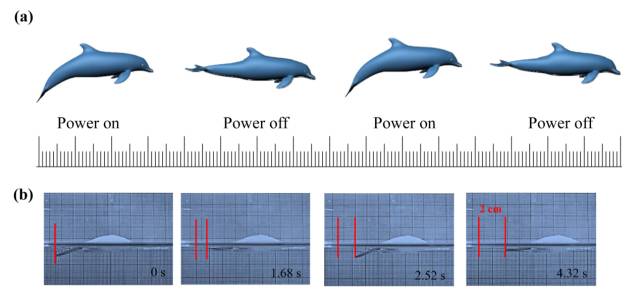
图2电驱动“游泳机器人”
摘要速递:
Construction of a Fish-like Robot Based on High Performance Graphene/PVDF Bimorph Actuation Materials
Advanced Science
DOI: 10.1002/advs.201500438
31 MAR 2016
Smart actuators have many potential applications in various areas, so the development of novel actuation materials, with facile fabricating methods and excellent performances, are still urgent needs. In this work, a novel electromechanical bimorph actuator constituted by a graphene layer and a PVDF layer, is fabricated through a simple yet versatile solution approach. The bimorph actuator can deflect toward the graphene side under electrical stimulus, due to the differences in coefficient of thermal expansion between the two layers and the converse piezoelectric effect and electrostrictive property of the PVDF layer. Under low voltage stimulus, the actuator (length: 20 mm, width: 3 mm) can generate large actuation motion with a maximum deflection of about 14.0 mm within 0.262 s and produce high actuation stress (more than 312.7 MPa/g). The bimorph actuator also can display reversible swing behavior with long cycle life under high frequencies. on this basis, a fish-like robot that can swim at the speed of 5.02 mm/s is designed and demonstrated. The designed graphene-PVDF bimorph actuator exhibits the overall novel performance compared with many other electromechanical avtuators, and may contribute to the practical actuation applications of graphene-based materials at a macro scale.
————高分子科学前沿



