它们看起来像一个个小小的、半透明的宝石,但是正是这些小小的凝胶条却包含了一个病人的肿瘤的整个微缩世界,并可以用于抗癌药物的测试以帮助科学家们在肿瘤和治疗之间找到最佳匹配。
实际上,这种“凝胶”是昆士兰科技大学(QUT)的研究人员们开发的一种全新的3D打印材料。这种材料能使科学家们针对目标肿瘤进行多重、同步测试以找到正确的治疗方式,从而为快速、个性化的癌症治疗开辟了道路。

据QUT健康与生物医学创新研究所(IHBI)的Dietmar W. Hutmacher教授称,这种新材料是一种明胶基水凝胶,可以用来模拟人体组织。
这种明胶基水凝胶的制造方法已经发表在了《Nature Protocols》杂志上。
“水凝胶是全世界研究人员普遍使用的生物材料;而明胶是基于胶原的,这是人体中最常见的组织之一。我们对明胶进行了修改以开发3D肿瘤微环境。”Hutmacher教授表示。
“我们的重大突破在于找到了一种方法可以以非常大的规模经济地制造这种高品质的材料。这种方法是高度重复性的,这意味着我们能够上百次地制造这种水凝胶,而不是在实验室中制造一次或两次,这样全世界的研究人员都能够制造它。”
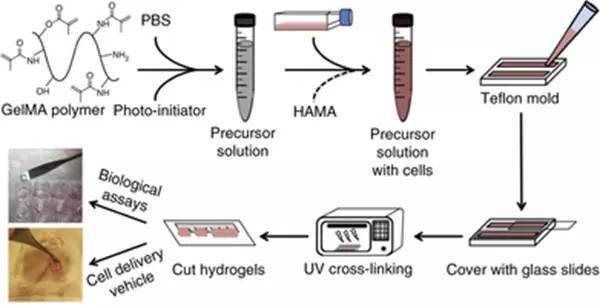
Hutmacher教授表示,这种新型的水凝胶,可以作为一种生物药水来3D打印微环境,或者打印肿瘤模型,以试验不同的抗癌药物。
“我们将能够用肿瘤细胞注入这种水凝胶,从而能够针对不同的病人快速创建一系列的肿瘤模型。
”目前人们为了治疗癌症进行的化疗往往属于运气式的,会影响到全身的细胞。而我们新开发的技术可以测试不同的抗癌药物及其所有的组合,这样我们可以制订出精确的个性化治疗方案,该方案只打击癌细胞。
“它将会把为每个病人找到一个个性化治疗方案的时间缩减到一周到两周。”
而且,科研人员还可以对水凝胶进行修改,以模仿软骨的硬度或柔软的乳腺组织;它可以用于创建所有类型癌症的模型,也可以拥有干细胞和组织工程的研究。
据了解,该新型水凝胶的发现实际上是Hutmacher教授领导的生物制造研究项目的一部分。Hutmacher教授所在的健康与生物医学创新研究所(IHBI)还曾经推出了世界上第一个生物制造硕士学位(Master of Biofabrication),这是澳大利亚和欧洲的一个双硕士学位。(天工社 编译自昆士兰科技大学)
摘要速递:
Functionalization, preparation and use of cell-laden gelatin methacryloyl–based hydrogels as modular tissue culture platforms
Nature Protocols
doi:10.1038/nprot.2016.037
Online 17 March 2016
Progress in advancing a system-level understanding of the complexity of human tissue development and regeneration is hampered by a lack of biological model systems that recapitulate key aspects of these processes in a physiological context. Hence, growing demand by cell biologists for organ-specific extracellular mimics has led to the development of a plethora of 3D cell culture assays based on natural and synthetic matrices. We developed a physiological microenvironment of semisynthetic origin, called gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA)-based hydrogels, which combine the biocompatibility of natural matrices with the reproducibility, stability and modularity of synthetic biomaterials. We describe here a step-by-step protocol for the preparation of the GelMA polymer, which takes 1–2 weeks to complete, and which can be used to prepare hydrogel-based 3D cell culture models for cancer and stem cell research, as well as for tissue engineering applications. We also describe quality control and validation procedures, including how to assess the degree of GelMA functionalization and mechanical properties, to ensure reproducibility in experimental and animal studies.
————来源:高分子科学前沿



